
Transform Your Health with Nature’s Most Powerful Foods
Are you tired of feeling sluggish, getting sick often, or struggling with low energy? This comprehensive guide reveals 50 nutrient-rich healthy foods that can completely change how you feel and function every day.
I have made this guide for busy professionals, health-conscious parents, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone ready to upgrade their eating habits without complicated meal plans or expensive supplements.
You’ll discover the science behind nutrient density and why it matters more than counting calories. We’ll explore power-packed vegetables and superfruits that boost your immune system and brain power naturally. You’ll also learn about the best foods for building muscle, supporting metabolism, and creating a balanced nutrition diet that actually fits your lifestyle.
From ancient grains that provide lasting energy to herbs and spices that work like natural medicine, each food on this list has been chosen for its proven health benefits. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to build a balanced diet using these nutritional powerhouses to feel your absolute best.
Understanding Nutrient Density and Its Impact on Your Body
How Nutrient-Dense Foods Maximize Health Benefits Per Calorie
Nutrient density represents the concentration of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds relative to the caloric content of food. Think of it as getting the biggest nutritional bang for your caloric buck. When you choose healthy foods with high nutrient density, you’re essentially fueling your body with premium gas instead of regular unleaded.
Dense nutrients pack multiple health-promoting compounds into fewer calories. A cup of spinach contains just 7 calories but delivers vitamin K, folate, iron, and powerful antioxidants. Compare this to a 150-calorie candy bar that offers mostly sugar and artificial additives. Your body receives exponentially more nutritional value from the spinach while consuming 95% fewer calories.
This concept becomes crucial for weight management and overall health. Your body requires specific amounts of vitamins and minerals daily, regardless of your caloric intake. When you consistently choose nutrient-dense options, you satisfy these requirements while maintaining or reducing caloric consumption. This approach naturally leads to better energy levels, improved immune function, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Best foods for maximizing nutrient density include:
- Dark leafy greens (kale, spinach, arugula)
- Colorful berries and citrus fruits
- Wild-caught fish and grass-fed meats
- Nuts, seeds, and legumes
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, Brussels sprouts)
The Science Behind Nutrient Absorption and Bioavailability
Bioavailability determines how effectively your body can absorb and utilize nutrients from different foods. Not all nutrients are created equal – some are readily absorbed while others require specific conditions or companion nutrients to become accessible to your cells.
Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) need dietary fats for proper absorption. Eating carrots with olive oil dramatically increases beta-carotene absorption compared to eating them plain. Water-soluble vitamins (B-complex, C) absorb more easily but are also eliminated quickly, requiring regular replenishment through your diet.
Mineral absorption depends heavily on your body’s current status and the presence of other compounds. Iron from plant sources (non-heme iron) absorbs better when paired with vitamin C-rich foods like bell peppers or strawberries. However, calcium can actually inhibit iron absorption, which explains why nutritionists recommend spacing out dairy and iron-rich meals.
Your gut health directly impacts nutrient absorption. A healthy microbiome produces enzymes that break down complex compounds and create an optimal environment for nutrient uptake. Processed foods often disrupt this delicate balance, while whole foods support beneficial bacteria growth.
Cooking methods also influence bioavailability. Light steaming can increase lycopene availability in tomatoes, while excessive heat destroys heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and some B vitamins.
Why Processed Foods Fail to Deliver Essential Nutrients
Processing strips away many naturally occurring nutrients while adding artificial preservatives, colors, and flavor enhancers that provide zero nutritional value. When grains are refined into white flour, the nutrient-rich germ and bran are removed, leaving mostly empty calories behind. Food manufacturers sometimes add synthetic vitamins back in, but these isolated nutrients lack the cofactors and synergistic compounds found in whole foods.
The processing journey often involves high heat, chemical treatments, and extended storage times that degrade sensitive nutrients. Vitamin C, for example, breaks down rapidly when exposed to air, light, and heat. Fresh fruits lose minimal vitamin C, while processed fruit products can lose up to 90% of their original content.
Processed foods typically contain high amounts of added sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats that actually increase your body’s nutrient requirements. Sugar metabolism depletes B vitamins and minerals like chromium and magnesium. Trans fats interfere with essential fatty acid metabolism, while excessive sodium can increase calcium excretion.
A balanced diet emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods that retain their natural nutrient profiles. These foods provide nutrients in their most bioavailable forms, surrounded by the cofactors and phytonutrients that enhance absorption and utilization. Balanced nutrition diet principles focus on choosing foods as close to their natural state as possible, ensuring maximum nutritional benefit from every bite.
Power-Packed Vegetables That Boost Immunity and Energy
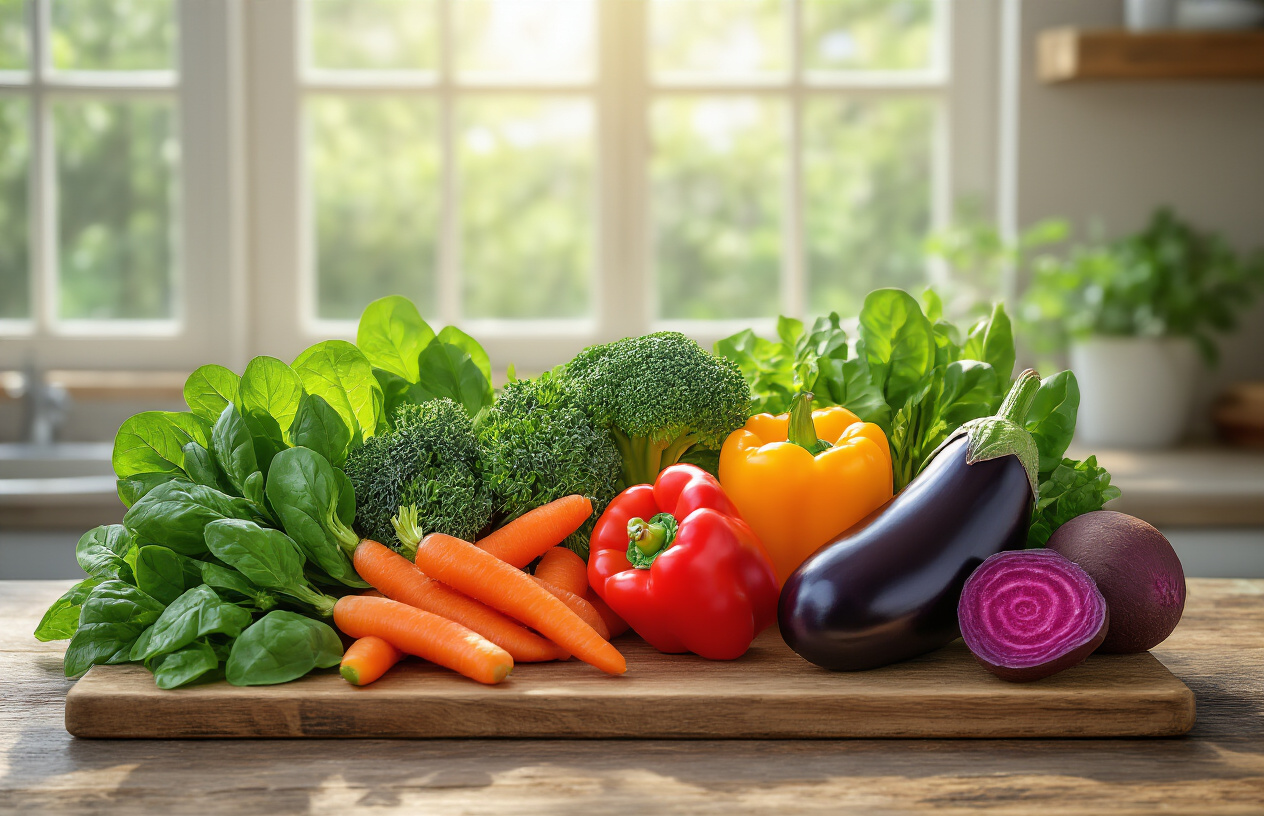

Leafy Greens That Fight Inflammation and Support Brain Health
Dark leafy greens pack more nutrients per calorie than almost any other food group, making them essential components of balanced nutrition diet plans. Spinach leads the charge with its impressive folate content, supporting cognitive function and reducing homocysteine levels linked to brain aging. One cup provides over 180% of your daily vitamin K needs, crucial for brain health and blood clotting.
Kale deserves its superfood status with exceptional vitamin C content – more than oranges per serving. Its glucosinolates break down into compounds that cross the blood-brain barrier, potentially protecting against neurodegenerative diseases. The lutein and zeaxanthin in kale also shield your brain from oxidative stress.
Swiss chard brings vibrant colors and powerful anti-inflammatory betalains to your plate. These compounds help reduce chronic inflammation that contributes to brain fog and fatigue. Arugula’s peppery bite comes from glucosinolates that support detoxification pathways, helping clear inflammatory compounds from your system.
Romaine lettuce might seem mild, but it contains significant amounts of folate and vitamin A. These nutrients work together to maintain healthy neurotransmitter production and protect brain cells from damage.
| Green | Key Nutrients | Brain Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Spinach | Folate, Iron, Vitamin K | Memory support, cognitive protection |
| Kale | Vitamin C, Lutein, Glucosinolates | Antioxidant defense, inflammation reduction |
| Swiss Chard | Betalains, Magnesium, Potassium | Stress reduction, neural function |
Cruciferous Vegetables for Cancer Prevention and Detoxification
Cruciferous vegetables contain unique sulfur compounds called glucosinolates that transform into powerful cancer-fighting molecules when chopped, chewed, or cooked. Broccoli stands out with high concentrations of sulforaphane, which activates your body’s detoxification enzymes and helps eliminate potential carcinogens.
Brussels sprouts might be polarizing, but they’re nutritional goldmines containing more glucosinolates than most vegetables. These tiny cabbages support liver detoxification and may help prevent hormone-related cancers. Their fiber content also feeds beneficial gut bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids, supporting overall immune function.
Cauliflower’s versatility makes it perfect for replacing refined carbs while delivering cancer-protective compounds. Its choline content supports liver function and fat metabolism, while indole-3-carbinol helps balance estrogen levels naturally.
Cabbage fermented into sauerkraut or kimchi multiplies its health benefits. The fermentation process creates probiotics that support gut health, while preserving the cancer-fighting compounds. Red cabbage contains additional anthocyanins that provide antioxidant protection.
- Optimal preparation: Lightly steam or eat raw to preserve glucosinolates
- Timing matters: Wait 10 minutes after chopping before cooking to maximize compound formation
- Pair wisely: Combine with healthy fats to enhance absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
Colorful Root Vegetables That Stabilize Blood Sugar
Root vegetables offer complex carbohydrates that provide steady energy without dramatic blood sugar spikes. Sweet potatoes rank among the best foods for sustained energy, with their orange flesh indicating high beta-carotene content. Their fiber slows sugar absorption, while potassium supports healthy blood pressure.
Beets contain natural nitrates that convert to nitric oxide, improving blood flow and potentially enhancing exercise performance. Their deep red pigments called betalains reduce inflammation and support liver detoxification. Beet juice has shown promise in lowering blood pressure and improving cognitive function.
Carrots provide more than just beta-carotene – they contain unique polyacetylenes with anti-inflammatory properties. Their natural sweetness satisfies cravings while delivering steady energy. Purple carrots add anthocyanins to the mix, offering additional antioxidant protection.
Turnips and parsnips are often overlooked but provide excellent nutrition. Turnips are low in calories but high in vitamin C and fiber, while parsnips offer folate and potassium. Both contain compounds that support healthy blood sugar regulation.
Blood Sugar Benefits:
- Natural fiber slows glucose absorption
- Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy
- Antioxidants protect against diabetes-related damage
- Potassium supports insulin sensitivity
Antioxidant-Rich Peppers and Tomatoes for Heart Protection
Bell peppers deliver more vitamin C than citrus fruits, with red peppers containing the highest concentrations. This vitamin C works synergistically with other antioxidants to protect blood vessels from damage and support collagen production. The capsanthin in red peppers may help reduce LDL cholesterol oxidation, a key factor in heart disease development.
Tomatoes shine with lycopene, a powerful carotenoid that becomes more bioavailable when cooked. This compound helps protect against cardiovascular disease and may reduce inflammation in blood vessels. Cherry tomatoes pack concentrated nutrition in small packages, making them perfect for snacking or adding to balanced diet meals.
Hot peppers bring heat along with capsaicin, which may boost metabolism and support heart health. Studies suggest capsaicin can help reduce blood pressure and improve circulation. Even mild peppers like poblanos provide these benefits without overwhelming heat.
Yellow and orange peppers contain unique carotenoids that work differently from their red counterparts. These compounds support eye health while providing cardiovascular protection. Their natural sweetness makes them appealing to those transitioning to healthier foods.
The synergy between peppers and tomatoes creates powerful antioxidant combinations. Cooking them together, as in many Mediterranean dishes, enhances nutrient absorption and provides comprehensive heart protection. These vegetables form the foundation of heart-healthy eating patterns worldwide.
Superfruits That Enhance Longevity and Mental Clarity
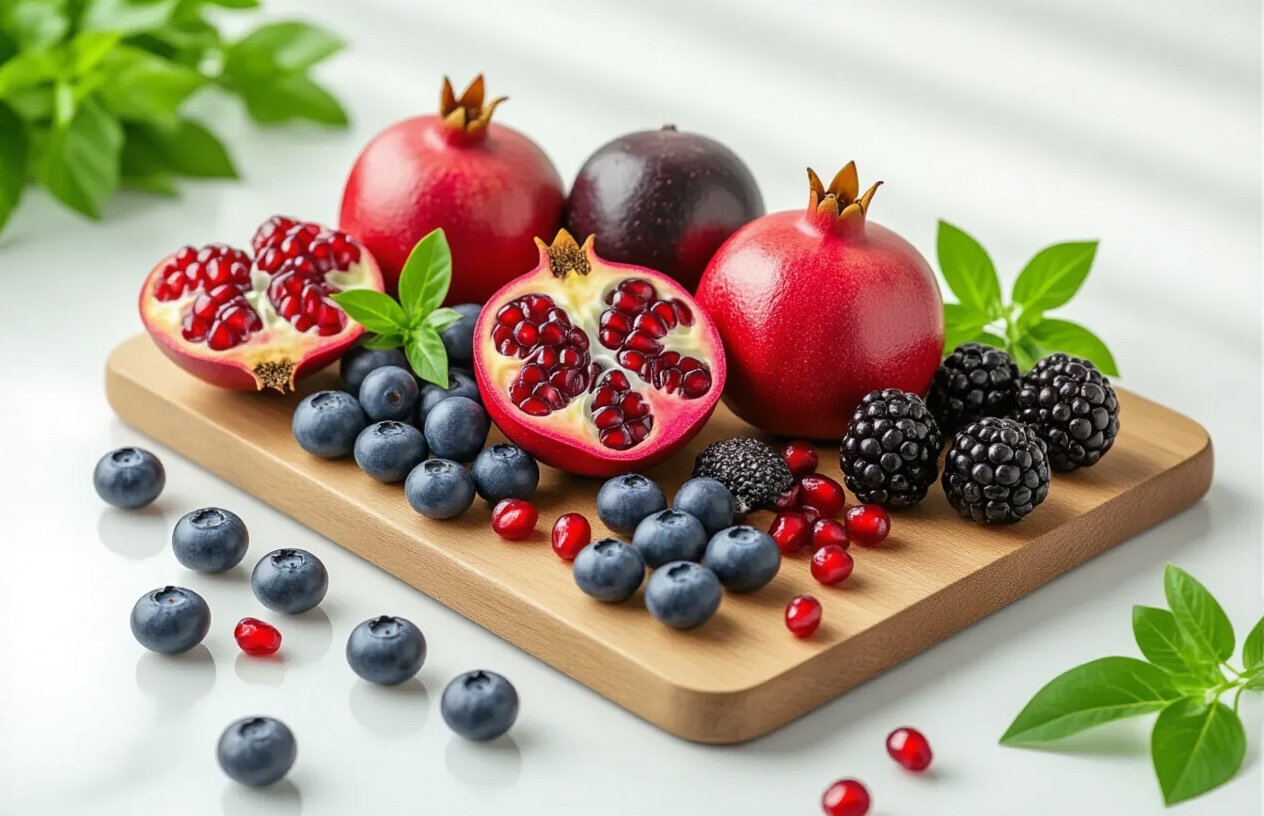

Berry Varieties That Protect Against Cognitive Decline
Blueberries reign supreme as brain-boosting healthy foods that pack an incredible antioxidant punch. These tiny powerhouses contain anthocyanins, compounds that cross the blood-brain barrier and accumulate in brain regions responsible for learning and memory. Research shows that people who eat blueberries regularly demonstrate improved memory performance and delayed cognitive aging.
Blackberries and raspberries deliver similar benefits with their rich anthocyanin profiles. Blackberries contain higher levels of ellagic acid, which protects neurons from oxidative stress and inflammation. Raspberries provide ketones that support fat metabolism in the brain, keeping neural pathways clear and functioning optimally.
Strawberries offer unique fisetin compounds that activate pathways linked to long-term memory formation. Their vitamin C content supports collagen production in blood vessels, ensuring healthy circulation to the brain. Goji berries, often called the “longevity fruit,” contain zeaxanthin that protects against age-related cognitive decline and supports visual processing areas in the brain.
| Berry Type | Key Compounds | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Blueberries | Anthocyanins | Memory enhancement |
| Blackberries | Ellagic acid | Neuroprotection |
| Raspberries | Ketones | Brain metabolism |
| Strawberries | Fisetin | Memory formation |
| Goji berries | Zeaxanthin | Visual cognition |
Citrus Fruits for Vitamin C and Immune System Support
Oranges deliver more than just vitamin C – they provide flavonoids like hesperidin that strengthen capillary walls and improve blood flow throughout the body. This enhanced circulation benefits both immune system function and cognitive performance. The folate in oranges supports neurotransmitter production, directly impacting mood and mental clarity.
Grapefruits contain unique compounds called limonoids that activate detoxification enzymes in the liver. This cleansing effect reduces the toxic burden on your body, allowing your immune system to focus on protecting against pathogens rather than dealing with accumulated waste products. Pink and red varieties offer additional lycopene, the same antioxidant that makes tomatoes heart-healthy.
Lemons and limes provide citric acid that enhances mineral absorption, particularly iron and calcium. Better mineral status translates to improved immune function and stronger bones. Their essential oils contain d-limonene, which supports liver detoxification and has anti-inflammatory properties that benefit the entire body.
Tangerines and mandarins offer easily absorbed vitamin C along with beta-cryptoxanthin, a carotenoid that converts to vitamin A in the body. This dual action supports both immune cell production and the integrity of mucous membranes – your body’s first line of defense against invading pathogens.
Exotic Fruits That Deliver Unique Phytonutrients
Pomegranates contain punicalagins, powerful antioxidants that surpass green tea and red wine in their potency. These compounds support cardiovascular health by protecting arteries from oxidative damage and reducing inflammation. The ellagic acid in pomegranate seeds helps regulate blood sugar levels and supports healthy cell division.
Dragon fruit provides betalains, vibrant pigments with anti-inflammatory properties that rival those found in beets. Its high magnesium content supports over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, including those involved in energy production and protein synthesis. The small black seeds add omega-3 fatty acids that support brain health.
Mangosteen, known as the “queen of fruits,” delivers xanthones – unique antioxidants found nowhere else in nature. These compounds demonstrate remarkable anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Traditional medicine has used mangosteen for centuries to support digestive health and boost overall vitality.
Passion fruit seeds contain piceatannol, a compound similar to resveratrol but with enhanced bioavailability. This antioxidant supports healthy aging at the cellular level and may help maintain cognitive function as you age. The pulp provides fiber that feeds beneficial gut bacteria.
Stone Fruits That Promote Healthy Digestion
Peaches and nectarines contain chlorogenic acid, the same beneficial compound found in coffee beans. This antioxidant supports healthy blood sugar regulation and provides anti-inflammatory benefits throughout the digestive tract. Their soft fiber content promotes regular bowel movements without causing digestive irritation.
Plums offer both soluble and insoluble fiber that feeds beneficial gut bacteria while promoting regularity. Their anthocyanins provide antioxidant protection to the intestinal lining, reducing inflammation that can interfere with nutrient absorption. Dried plums (prunes) concentrate these benefits while adding boron for bone health.
Apricots provide beta-carotene that converts to vitamin A, supporting the health of intestinal mucosa. Their potassium content helps maintain proper fluid balance in digestive tissues. Fresh apricots offer gentle fiber that soothes the digestive tract while providing steady energy release.
Cherries contain melatonin naturally, supporting healthy sleep cycles that allow your digestive system to rest and repair overnight. Their anti-inflammatory compounds reduce oxidative stress in digestive organs. Tart cherries specifically provide higher concentrations of beneficial anthocyanins that support overall gut health and may reduce exercise-induced inflammation.
Protein Sources That Build Muscle and Support Metabolism
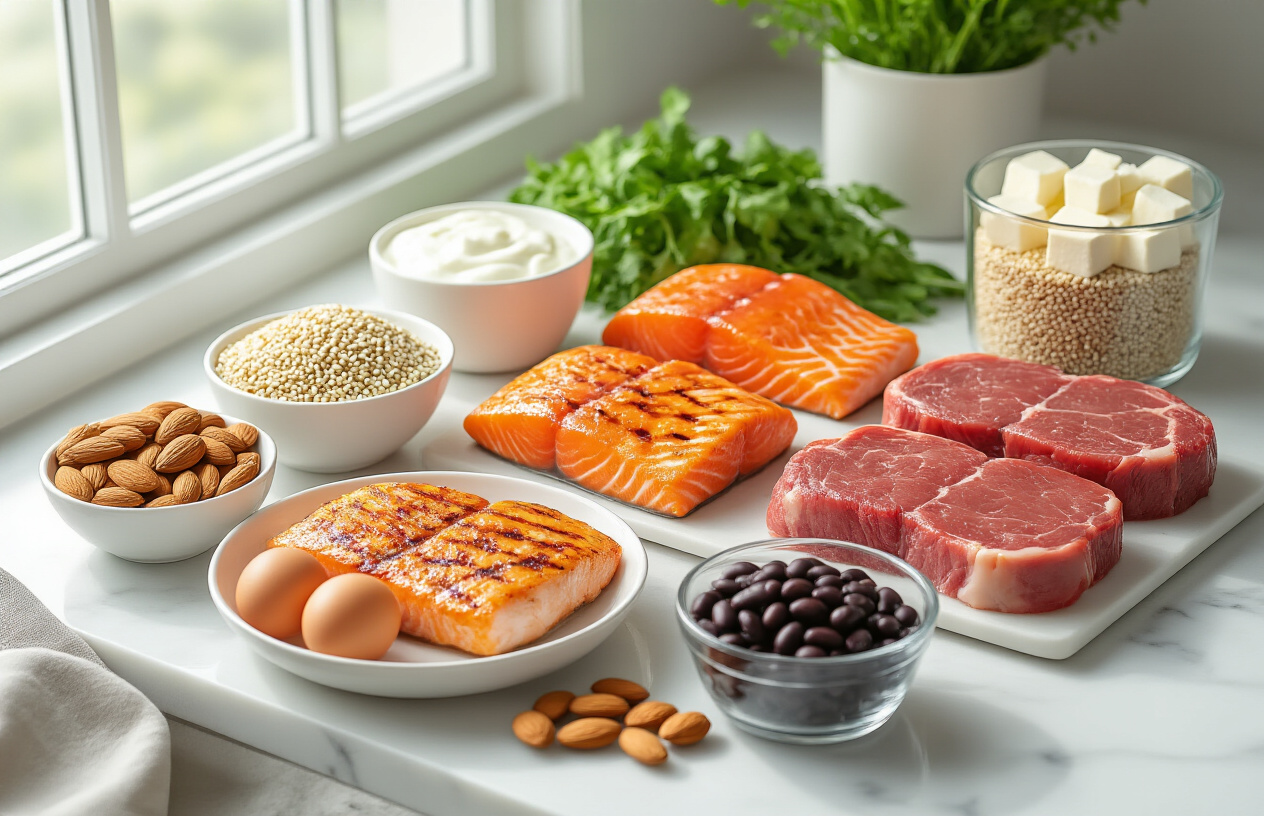

Wild-Caught Fish Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Wild-caught salmon stands out as the ultimate protein powerhouse, delivering about 25 grams of complete protein per 3.5-ounce serving while flooding your system with EPA and DHA omega-3s. These essential fatty acids don’t just support brain health – they actively reduce muscle inflammation after intense workouts, speeding up recovery time significantly.
Sardines pack an incredible nutritional punch despite their small size. Just one can provides over 20 grams of protein plus a hefty dose of vitamin B12 and selenium. The bonus? They’re at the bottom of the food chain, meaning minimal mercury contamination compared to larger predatory fish.
Mackerel offers another excellent option for those seeking healthy foods that support metabolism. This oily fish contains high levels of coenzyme Q10, which helps your cells produce energy more efficiently. The protein quality matches that of any land-based source while providing unique marine nutrients you simply can’t get elsewhere.
| Fish Type | Protein (per 100g) | Omega-3 Content | Mercury Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild Salmon | 25g | Very High | Low |
| Sardines | 25g | High | Very Low |
| Mackerel | 19g | Very High | Low |
| Anchovies | 20g | High | Very Low |
Grass-Fed Meats for Complete Amino Acid Profiles
Grass-fed beef contains all nine essential amino acids your body needs to build and repair muscle tissue. The key difference from grain-fed varieties lies in the superior fatty acid profile – grass-fed meat provides up to five times more omega-3 fatty acids and higher levels of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which research shows can help reduce body fat while preserving lean muscle mass.
Bison represents one of nature’s cleanest protein sources. These animals roam freely and eat their natural diet, resulting in meat that’s naturally leaner than conventional beef yet richer in iron, zinc, and B vitamins. A 4-ounce serving delivers 24 grams of protein with significantly less saturated fat than grain-fed alternatives.
Lamb from pasture-raised animals offers unique nutritional benefits often overlooked in discussions about best foods for muscle building. This red meat provides exceptional amounts of zinc and selenium – minerals crucial for testosterone production and cellular repair. The protein digestibility score matches that of eggs, making it highly bioavailable for muscle synthesis.
Plant-Based Proteins That Reduce Inflammatory Markers
Hemp seeds deserve recognition as a complete plant protein containing all essential amino acids in optimal ratios. Three tablespoons provide 10 grams of easily digestible protein plus gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), an anti-inflammatory omega-6 fatty acid that most people lack in their diet. Unlike many plant proteins, hemp doesn’t cause digestive distress and actually supports gut health.
Quinoa stands apart from other grains because it’s technically a seed with complete protein status. One cup of cooked quinoa delivers 8 grams of protein along with lysine – an amino acid typically missing in plant foods. This makes quinoa particularly valuable for anyone following a balanced nutrition diet focused on plant-based sources.
Lentils provide an impressive protein-to-calorie ratio while offering substantial amounts of folate, iron, and fiber. Red lentils cook quickly and blend seamlessly into soups and stews, while black beluga lentils hold their shape beautifully in salads. Research shows regular lentil consumption can help reduce C-reactive protein levels, a key marker of systemic inflammation.
Spirulina, though technically a blue-green algae, contains 60-70% protein by weight – more than any other whole food. This superfood provides all essential amino acids plus unique compounds like phycocyanin, which has powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Just one tablespoon mixed into smoothies adds 4 grams of highly bioavailable protein.
Eggs and Dairy from Pasture-Raised Animals
Pasture-raised eggs represent the gold standard for protein quality, with a perfect amino acid score of 100. These eggs contain significantly higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin E, and beta-carotene compared to conventional cage-raised varieties. The yolks are noticeably more vibrant in color, reflecting their superior nutrient density.
Greek yogurt from grass-fed cows provides double the protein of regular yogurt while delivering beneficial probiotics that support digestive health and immune function. The straining process removes much of the lactose, making it easier to digest for those with mild dairy sensitivities. Choose varieties with no added sugars to maximize the metabolic benefits.
Raw milk cheeses from pasture-raised animals offer concentrated nutrition in small portions. Hard cheeses like aged cheddar or gouda provide 6-8 grams of protein per ounce along with vitamin K2, which works synergistically with vitamin D to support bone health and proper calcium utilization.
Cottage cheese made from grass-fed milk supplies casein protein, which digests slowly and provides a steady stream of amino acids to your muscles over several hours. This makes it an ideal choice for evening meals or pre-bedtime snacks when following a balanced diet focused on muscle preservation and recovery.
Healthy Fats That Optimize Brain Function and Hormone Production
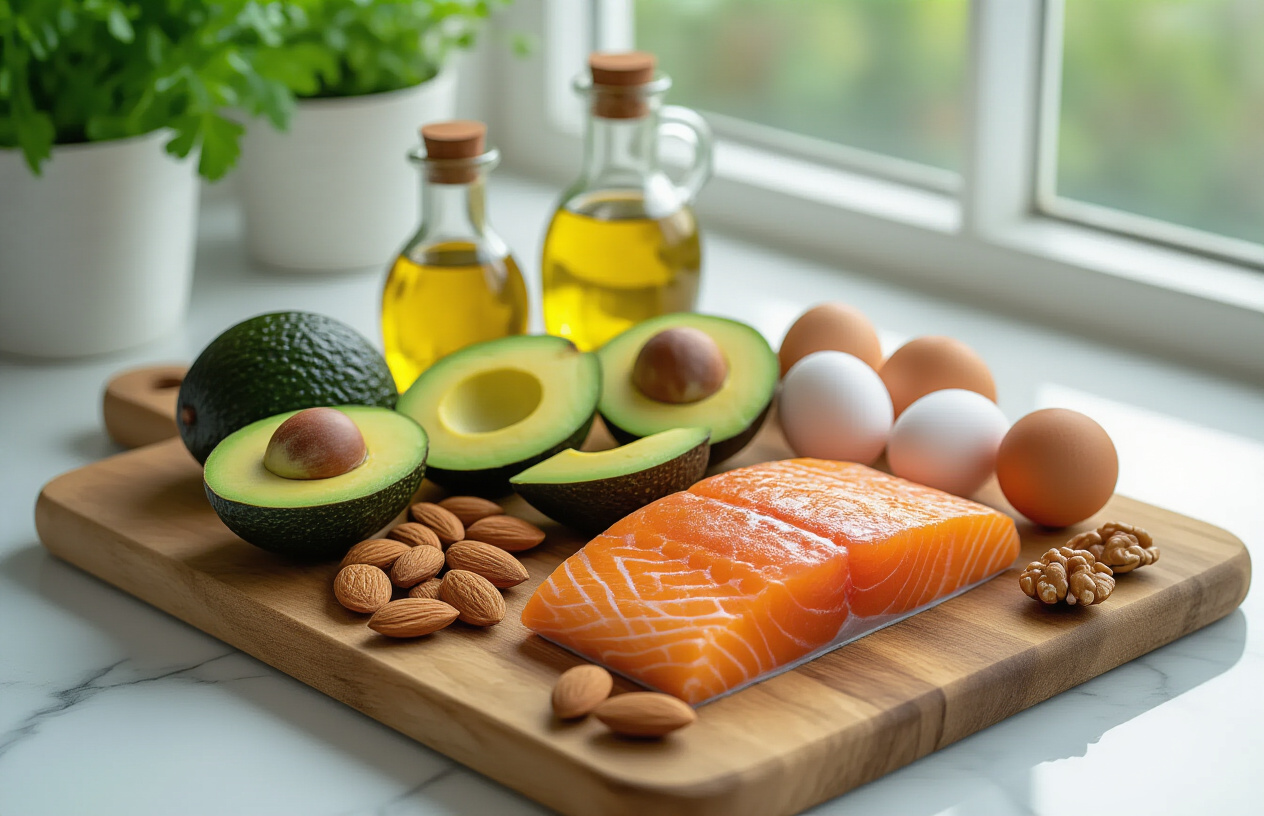

Nuts and Seeds for Essential Fatty Acid Balance
Nuts and seeds pack serious nutritional punch when it comes to supporting brain health and hormone production. These small but mighty healthy foods contain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids that your body can’t make on its own. Walnuts stand out as brain-boosting champions, containing alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) that converts to DHA – the same fatty acid found in fish oil. Just a quarter cup provides nearly your entire daily omega-3 needs.
Chia seeds deserve special recognition for their impressive omega-3 content. Two tablespoons deliver more than 4 grams of these essential fats, plus fiber and protein that help stabilize blood sugar. Flaxseeds offer similar benefits but require grinding to unlock their nutritional potential. Hemp seeds provide the perfect 3:1 ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids, making them ideal for hormone balance.
Almonds and Brazil nuts bring selenium and vitamin E to the table – powerful antioxidants that protect your brain cells from oxidative stress. Pumpkin seeds supply zinc, which plays a crucial role in neurotransmitter production and hormone regulation. Sunflower seeds offer vitamin E and healthy fats that support cognitive function.
The key is variety. Rotating different nuts and seeds ensures you get a full spectrum of beneficial fats and nutrients. Raw or lightly roasted options retain more of their nutritional value compared to heavily processed varieties loaded with salt or sugar.
Avocados and Olives for Monounsaturated Fat Benefits
Avocados have earned their superfood status through their rich monounsaturated fat content, particularly oleic acid. This healthy fat reduces inflammation in the brain and supports the production of myelin – the protective coating around nerve fibers that speeds up neural communication. One medium avocado provides about 20 grams of monounsaturated fats along with fiber, potassium, and folate.
These creamy fruits also enhance nutrient absorption. The fats in avocados help your body absorb fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K from other foods in your meal. This makes avocados perfect additions to salads loaded with colorful vegetables – you’ll actually absorb more nutrients from those leafy greens and tomatoes.
Olives and extra virgin olive oil bring similar benefits with their high oleic acid content. The Mediterranean diet’s emphasis on olive oil correlates with lower rates of cognitive decline and better hormone balance. Cold-pressed extra virgin olive oil retains more antioxidants like vitamin E and polyphenols that protect against brain aging.
Kalamata, Castelvetrano, and green olives each offer unique flavor profiles while delivering healthy monounsaturated fats. The sodium content in olives actually helps with electrolyte balance, supporting proper nerve function. Olive oil works best when used cold or at low temperatures to preserve its beneficial compounds.
These foods support hormone production by providing the building blocks for steroid hormones like testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol. Your endocrine system relies on adequate healthy fat intake to function optimally.
Coconut and MCT Oils for Quick Energy and Ketone Production
Coconut oil contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) that behave differently from other fats in your body. These unique fatty acids bypass normal fat digestion and go straight to your liver, where they convert quickly into ketones – an alternative fuel source for your brain. This rapid conversion makes coconut oil excellent for immediate energy without the blood sugar spike.
MCT oil takes this concept further by concentrating the most beneficial medium-chain fatty acids: caprylic acid (C8) and capric acid (C10). These specific MCTs cross the blood-brain barrier efficiently, providing your brain cells with immediate fuel. Many people notice improved mental clarity and focus within 30-60 minutes of consuming MCT oil.
The ketone production from MCTs offers neuroprotective benefits. Ketones provide a more efficient energy source for brain cells compared to glucose, potentially supporting memory formation and cognitive function. Research suggests regular MCT consumption may help protect against age-related cognitive decline.
For hormone production, MCTs provide the raw materials needed for steroid hormone synthesis. The quick energy they provide can also help reduce cortisol levels by supporting stable blood sugar, which reduces stress on your endocrine system.
Start slowly with MCT oil – begin with one teaspoon daily to avoid digestive upset. Coconut oil offers a gentler introduction with about 60% MCT content compared to pure MCT oil. Both integrate easily into coffee, smoothies, or salad dressings. Virgin coconut oil retains more beneficial compounds, while refined versions have a neutral taste that some prefer for cooking.
These best foods for brain and hormone health work synergistically when combined in a balanced diet, supporting optimal cognitive function and endocrine health.
Ancient Grains and Legumes That Sustain Energy Levels
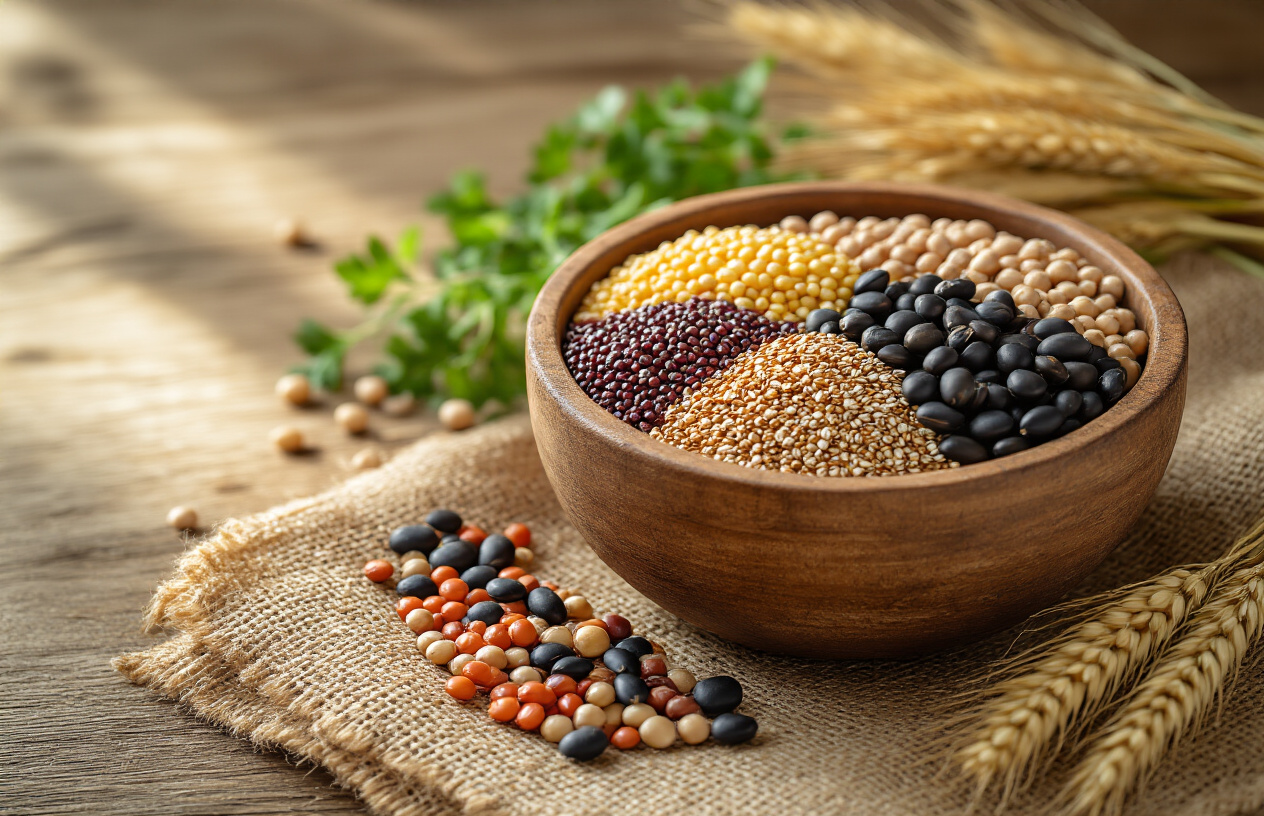

Quinoa and Amaranth for Complete Protein and Fiber
Quinoa stands out among healthy foods as one of the few plant sources that delivers all nine essential amino acids your body can’t produce on its own. This ancient seed packs 8 grams of complete protein per cooked cup, making it perfect for anyone looking to build muscle without relying solely on animal products. The fiber content hits 5 grams per serving, helping stabilize blood sugar and keep you satisfied for hours.
Amaranth brings similar nutritional power with its impressive protein profile and adds unique benefits like lysine, an amino acid that many grains lack. Both grains cook quickly and absorb flavors beautifully, making them versatile additions to your balanced nutrition diet. Try quinoa in morning bowls with berries and nuts, or use amaranth as a creamy base for savory dishes.
The mineral content in these best foods includes magnesium for energy production, iron for oxygen transport, and phosphorus for strong bones. Unlike refined grains that spike blood sugar, quinoa and amaranth provide steady energy release thanks to their complex carbohydrate structure and high fiber content.
Sprouted Legumes That Improve Digestibility
Sprouting transforms legumes into nutritional powerhouses while reducing the compounds that cause digestive discomfort. When beans, lentils, and chickpeas sprout, their enzyme inhibitors break down, making nutrients more bioavailable and easier on your stomach. The sprouting process also increases vitamin C content significantly and reduces phytic acid, which can block mineral absorption.
Sprouted mung beans offer exceptional digestibility and cook in just 15 minutes compared to their unsprouted counterparts that need hours. Sprouted lentils become tender and nutty, perfect for salads and quick sautés. These foods fit seamlessly into any balanced diet, providing plant-based protein without the gas and bloating that sometimes comes with regular legumes.
The enhanced enzyme activity in sprouted legumes helps your body break down proteins more efficiently. This means better amino acid absorption and less strain on your digestive system. Sprouted chickpeas make fantastic hummus with a lighter texture, while sprouted black beans add protein to salads without weighing you down.
Fermented Grains That Support Gut Health
Fermented grains undergo transformation through beneficial bacteria that pre-digest complex starches and create probiotics. Sourdough bread made from ancient grains offers dramatically different nutritional benefits compared to commercial bread. The fermentation process breaks down gluten proteins and increases the bioavailability of B vitamins, particularly folate and B12 precursors.
Fermented oats, known as overnight oats with kefir or yogurt, create an ideal environment for beneficial gut bacteria. This preparation method reduces the grain’s natural phytic acid while adding live cultures that support digestive health. The combination creates one of the best foods for sustained energy and gut microbiome balance.
Traditional fermented grain preparations like Ethiopian injera or Indian idli demonstrate how cultures worldwide have used fermentation to maximize grain nutrition. These foods support a balanced nutrition diet by providing prebiotics that feed beneficial bacteria and probiotics that directly populate your gut with helpful microorganisms.
| Fermented Grain | Fermentation Time | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Sourdough starter | 5-7 days | Improved gluten breakdown, enhanced mineral absorption |
| Fermented oats | 8-12 hours | Increased B vitamins, probiotic activity |
| Kefir grains | 12-24 hours | Live cultures, reduced lactose content |
The gentle acidity from fermentation also helps your body absorb minerals like iron, zinc, and calcium more effectively than from regular grains.
Herbs and Spices That Act as Natural Medicine
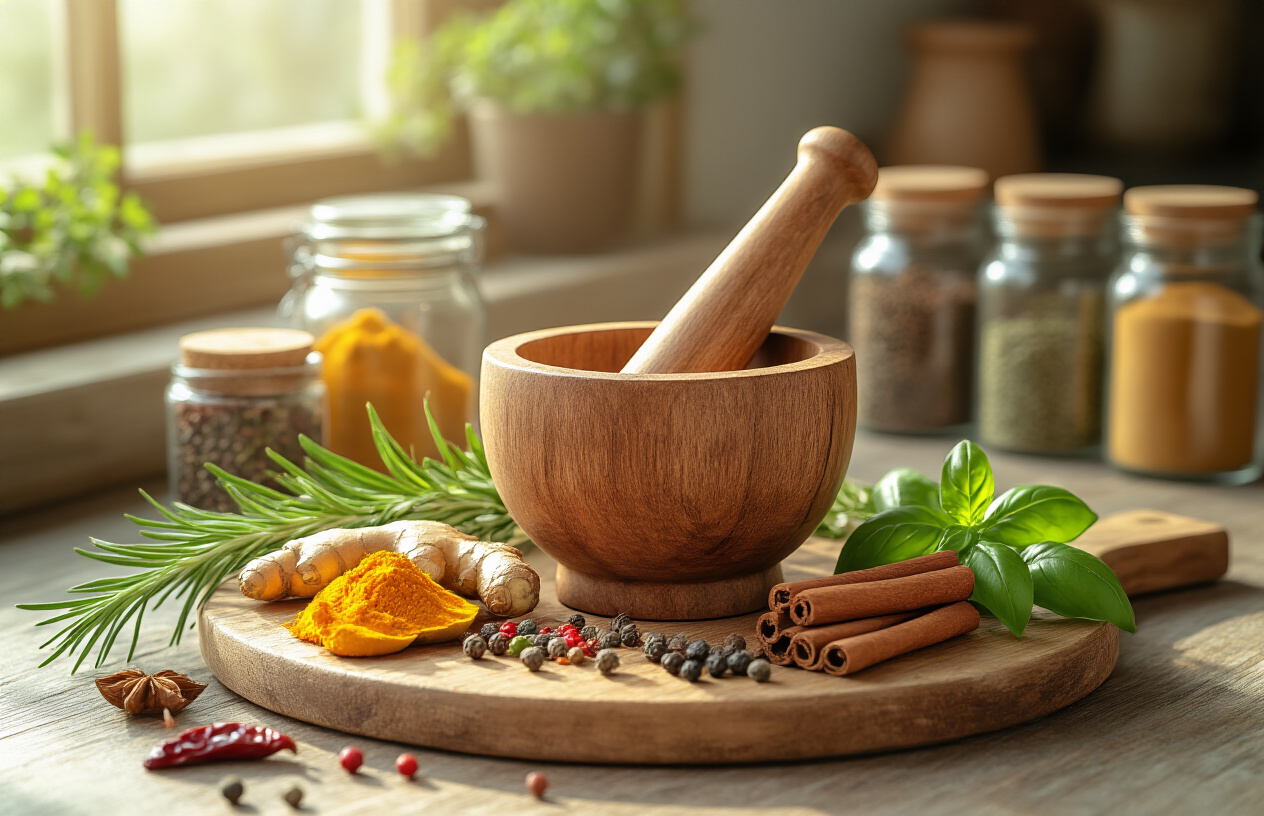

Anti-Inflammatory Turmeric and Ginger for Pain Relief
Turmeric and ginger stand out as two of nature’s most powerful pain-fighting allies. These golden roots contain bioactive compounds that rival prescription medications in their anti-inflammatory effects. Turmeric’s active ingredient, curcumin, blocks inflammatory pathways at the cellular level and has been shown to reduce joint pain by up to 60% in clinical studies. Adding just one teaspoon of turmeric to your daily routine can significantly lower inflammation markers in your blood.
Ginger works differently but equally effectively, containing gingerols and shogaols that interrupt pain signals before they reach your brain. Fresh ginger root provides the most potent effects, though dried ginger powder still packs a serious punch. Many people find relief from chronic conditions like arthritis, muscle soreness, and even migraines by incorporating these healthy foods into their balanced nutrition diet.
For maximum benefit, combine turmeric with black pepper, which increases curcumin absorption by 2000%. Try grating fresh ginger into smoothies, teas, or stir-fries. Both spices enhance the anti-inflammatory properties of other foods when used together in cooking.
Adaptogenic Herbs That Combat Stress and Fatigue
Adaptogenic herbs help your body adapt to stress while restoring natural energy levels. These remarkable plants work by regulating your adrenal glands and balancing cortisol production. Ashwagandha leads the pack, reducing stress hormones by 30% within just eight weeks of regular use. This ancient herb also improves sleep quality and mental clarity without causing drowsiness.
Rhodiola rosea excels at fighting fatigue and boosting physical endurance. Research shows it can increase work capacity by 20% while reducing mental fatigue during stressful periods. Holy basil, another powerful adaptogen, calms anxiety while supporting healthy blood sugar levels.
Ginseng varieties offer sustained energy without the crash associated with caffeine. Siberian ginseng particularly helps with recovery from illness or intense physical training. These best foods for stress management work gradually, building resilience over weeks rather than providing instant effects.
| Adaptogen | Primary Benefit | Recommended Daily Dose |
|---|---|---|
| Ashwagandha | Stress reduction | 300-600mg |
| Rhodiola | Energy boost | 200-400mg |
| Holy Basil | Anxiety relief | 300-600mg |
| Ginseng | Endurance | 200-400mg |
Aromatic Spices That Boost Metabolism and Circulation
Certain spices act as metabolic accelerators, naturally increasing your body’s calorie-burning capacity. Cayenne pepper contains capsaicin, which raises your metabolic rate by 5-10% for several hours after consumption. This thermogenic effect helps burn extra calories while improving circulation throughout your body.
Cinnamon stabilizes blood sugar levels and enhances insulin sensitivity, making it easier to maintain steady energy and prevent fat storage. Ceylon cinnamon provides the best results without the liver concerns associated with cassia cinnamon. Just half a teaspoon daily can improve glucose metabolism significantly.
Black pepper increases nutrient absorption from other foods while stimulating digestive fire. Its piperine content also breaks down fat cells and prevents new ones from forming. Cardamom supports healthy metabolism while freshening breath and settling digestion.
Mustard seeds contain compounds that boost metabolism for up to three hours after eating. Ground mustard works well in dressings and marinades. These metabolism-boosting spices complement a balanced diet by helping your body process nutrients more efficiently.
Fresh Herbs That Provide Concentrated Antioxidants
Fresh herbs contain some of the highest concentrations of antioxidants found in any foods. Oregano tops the charts with an antioxidant capacity that surpasses most fruits and vegetables. Fresh oregano provides 42 times more antioxidant activity than apples and four times more than blueberries.
Parsley delivers exceptional amounts of vitamin K, vitamin C, and flavonoids that protect against cellular damage. The chlorophyll in fresh parsley also helps detoxify your liver and blood. Cilantro excels at removing heavy metals from your system while providing unique antioxidants not found in other herbs.
Basil contains volatile oils that have anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Purple basil varieties offer even higher antioxidant levels than green basil. Fresh rosemary protects brain cells from oxidative stress and may improve memory and concentration.
Growing your own herbs ensures maximum freshness and potency. Even windowsill herb gardens can supply enough fresh herbs to significantly boost your antioxidant intake. These concentrated sources of protective compounds make excellent additions to any balanced nutrition diet focused on long-term health optimization.
Creating Balanced Meal Plans Using These Nutrient Powerhouses

Daily Meal Combinations That Maximize Nutrient Synergy
Pairing the right healthy foods creates powerful combinations that enhance absorption and boost your body’s ability to use nutrients effectively. Iron-rich spinach becomes even more powerful when combined with vitamin C from bell peppers or citrus fruits, increasing iron absorption by up to 300%. Similarly, mixing lycopene-rich tomatoes with healthy fats like olive oil or avocado helps your body absorb this cancer-fighting compound more efficiently.
Start your day with combinations like Greek yogurt topped with berries and nuts, providing probiotics, antioxidants, and healthy fats that work together. For lunch, pair leafy greens with seeds and colorful vegetables, drizzled with tahini or olive oil dressing. The fat helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K from the greens.
Smart dinner combinations include wild salmon with roasted sweet potatoes and broccoli – the omega-3s from fish enhance the absorption of beta-carotene from orange vegetables. Adding a squeeze of lemon provides vitamin C that helps your body use the iron from the broccoli more effectively.
Consider these synergistic pairings throughout your day:
- Turmeric with black pepper (increases curcumin absorption by 2000%)
- Green tea with lemon (boosts antioxidant availability)
- Beans with bell peppers (iron and vitamin C combination)
- Dark chocolate with almonds (healthy fats enhance flavonoid absorption)
Seasonal Eating Strategies for Optimal Freshness
Eating seasonally connects you with nature’s rhythm while providing the freshest, most nutrient-dense foods available. Spring brings detoxifying greens like dandelion, arugula, and asparagus – perfect for cleansing after winter’s heavier foods. These early greens contain higher concentrations of vitamins and minerals because they’re harvested at peak ripeness.
Summer abundance offers hydrating fruits and vegetables packed with antioxidants to protect against sun damage. Tomatoes, berries, stone fruits, and cucumbers provide natural cooling properties while delivering maximum nutrition. The high water content in summer produce helps maintain hydration during warmer months.
Fall’s harvest focuses on grounding foods rich in complex carbohydrates and warming spices. Squashes, root vegetables, and apples provide sustained energy and immune-boosting nutrients to prepare for winter. These best foods store well and provide comfort during cooler weather.
Winter calls for warming, nourishing foods that support immune function. Citrus fruits peak in vitamin C content, while stored roots and preserved foods provide sustained nutrition. Hearty soups combining seasonal vegetables with legumes create warming, nutrient-dense meals.
Shopping at farmers markets connects you directly with seasonal availability and often provides produce harvested within 24-48 hours, retaining maximum nutritional value compared to grocery store items that may have traveled thousands of miles.
Budget-Friendly Tips for Accessing Quality Whole Foods
Building a balanced nutrition diet doesn’t require breaking the bank when you know where to focus your spending. Buy conventionally grown produce for items with thick peels like avocados, bananas, and onions, while prioritizing organic purchases for thin-skinned fruits and leafy greens that absorb more pesticides.
Frozen vegetables and fruits often contain more nutrients than fresh ones that have traveled long distances or sat in storage. They’re picked at peak ripeness and flash-frozen, locking in vitamins and minerals. Stock up when sales occur and use them in smoothies, soups, and stir-fries.
Bulk buying works well for nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains – the foundation of any balanced diet. Store these properly in airtight containers to maintain freshness and nutritional value. Many health food stores offer bulk bins where you can purchase exactly what you need.
Cook larger batches and freeze portions for busy weeks. Batch-cooking grains, roasting vegetables, and preparing soups saves both time and money while ensuring you always have nutritious options available.
| Cost-Saving Strategy | Potential Savings | Best Items to Buy |
|---|---|---|
| Seasonal shopping | 30-50% | All produce |
| Bulk purchasing | 20-40% | Grains, legumes, nuts |
| Frozen over fresh | 15-25% | Berries, vegetables |
| Store brands | 10-30% | Canned goods, oils |
Community-supported agriculture (CSA) boxes provide seasonal variety at reduced costs while supporting local farmers. Many offer payment plans or work-share programs that make fresh, quality produce more accessible to any budget.

Eating nutrient-dense foods isn’t just about following the latest health trend – it’s about giving your body the fuel it needs to thrive. From immunity-boosting vegetables and brain-enhancing superfruits to muscle-building proteins and hormone-balancing healthy fats, these 50 powerhouse foods work together to transform how you feel every day. Add in ancient grains, legumes, and healing herbs, and you’ve got a complete toolkit for better health.
The real magic happens when you start building meals around these nutrient champions. You don’t need to overhaul your entire diet overnight. Start by swapping one processed food for a nutrient-rich alternative, experiment with a new superfruit in your morning smoothie, or add some immunity-boosting spices to your dinner. Small changes add up to big results, and your body will thank you for every colorful, nutrient-packed bite you take.
Disclaimer:
This article is for information and learning only. This article neither includes nor recommends any information about how to address medical, psychological, or financial issues. If you face severe stress, anxiety, and depression, please seek a qualified professional.
Written by Azhar Huzaifa
Azhar Huzaifa is the founder of LifeBalanceInsight.com.
He writes about money psychology, health, and life balance,
helping middle-class families reduce stress and live better lives.

